Knowledge Base
The AB Electronics UK Knowledge Base provides support solutions, tutorials and troubleshooting guides.

ADC Pi with HIH-4000
ADC Pi with HIH-4000 Series Humidity Sensor
This tutorial will use the ADC Pi or ADC Pi Plus with a Honeywell HIH-4000 Series Humidity Sensor to make a digital humidity reader. You will need your Raspberry Pi, an ADC Pi or ADC Pi Plus, and a Honeywell HIH-4000 Series Humidity Sensor.
We will use the AB Electronics Python library to talk to the ADC Pi. To download the library, visit our Python Library and Demos knowledge base article.
You must enable I2C on your Raspberry Pi; see our other tutorial on i2c: I2C, SMBus and Raspbian Linux.
The AB Electronics Python library uses another library called python3-smbus; you can install it using apt-get with the following commands.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python3-smbus
With the libraries installed and the Raspberry Pi configured to use I2C we can begin building our project.
Parts Used:
Honeywell HIH-4000 Series Humidity Sensor (Datasheet)
100K Resistor
Connecting the Sensor to the ADC Pi
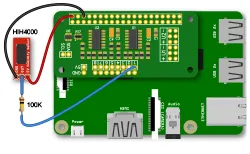 If you haven't done so, install your ADC Pi onto the Raspberry Pi by connecting it to the GPIO header. Make sure your Raspberry Pi is turned off when you do this to minimise the risk of damaging the Raspberry Pi or the ADC Pi.
If you haven't done so, install your ADC Pi onto the Raspberry Pi by connecting it to the GPIO header. Make sure your Raspberry Pi is turned off when you do this to minimise the risk of damaging the Raspberry Pi or the ADC Pi.
Next, connect the HIH4000 sensor to the ADC Pi. Pin 1 connects to +5V, Pin 2 connects to input 1 on the ADC Pi via a 100K resistor, and Pin 3 connects to GND.
We will create a new Python program file for this tutorial called demo-hih4000.py. You can use your favourite text editor to write the program. A complete example of demo-hih4000.py is available in the ABElectronics_Python_Libraries/ADCPI/demos/ folder. Please note the version in the demos folder contains some extra code to check if the ADCPi library has been installed.
At the top of your program, we must import the ADCPI and the time library. We also add variables to hold the values related to the sensor data conversion.
#!/usr/bin/env python from ADCPi import ADCPi import time resistor_multiplier = 6.95225 # use 100K resistor in series with the input zero_offset = 0.826 # zero offset value from calibration data printout slope = 0.031483 # slope value from calibration data printout
The ADCPI library is used for all communication with your ADC Pi; it gives you control over almost everything that can be done with the MCP3424 controller.
Create an instance of the ADCPI class and call it adc.
adc = ADCPi(0x68, 0x69, 18)
0x68 and 0x69 are the I2C addresses for the ADC chips; if you have changed the address selection jumpers on your ADC Pi, you must change these numbers to match the new addresses.
Now create a function to calculate the humidity based on the voltage output from the ADC Pi.
def calcHumidity(inval):
voltage = inval * resistor_multiplier
humidity = (voltage - zero_offset) / slope
return humidity
We will need a loop so that the same commands can run repeatedly. This can be done with a simple while loop.
while True:
As True is always true, the while loop will continue until you exit the program with a Ctrl-C.
We must issue a clear command to clear the console for each read.
# clear the console
os.system('clear')
Next, we read from channel 1 on the ADC Pi and use the calcHumidity function to convert the voltage to humidity and print it to the console.
# read from adc channels and print to screen
print ("Humidity on channel 1: %0.1f%%" % calcHumidity(adc.read_voltage(1)))
Using the time.sleep method, we add a 0.5-second delay before repeating the read.
time.sleep(0.5)
time.sleep takes one variable, a number representing the number of seconds to wait. 1 will make the program sleep for 1 second while 0.1 would wait for 100ms.
That is everything we need to make read from the TMP36 sensor using your ADC Pi; your program should now look like this.
#!/usr/bin/python
from ADCPi import ADCPi
import time
import os
resistor_multiplier = 6.95225 # use 100K resistor in series with the input
zero_offset = 0.826 # zero offset value from calibration data printout
slope = 0.031483 # slope value from calibration data printout
adc = ADCPi(0x68, 0x69, 18)
def calc_humidity(inval):
voltage = inval * resistor_multiplier
humidity = (voltage - zero_offset) / slope
return humidity
while True:
# clear the console
os.system('clear')
# read from adc channels and print to screen
print("Humidity on channel 1: %0.1f%%" % calc_humidity(adc.read_voltage(1)))
# wait 0.5 seconds before reading the pins again
time.sleep(0.5)
Save your program as "demo_hih4000.py" and run it in a command terminal.
python3 demo_hih4000.py
You will now have a humidity reading from your sensor on the console, which updates twice a second.
(images created with Fritzing)
Related Expansion Boards