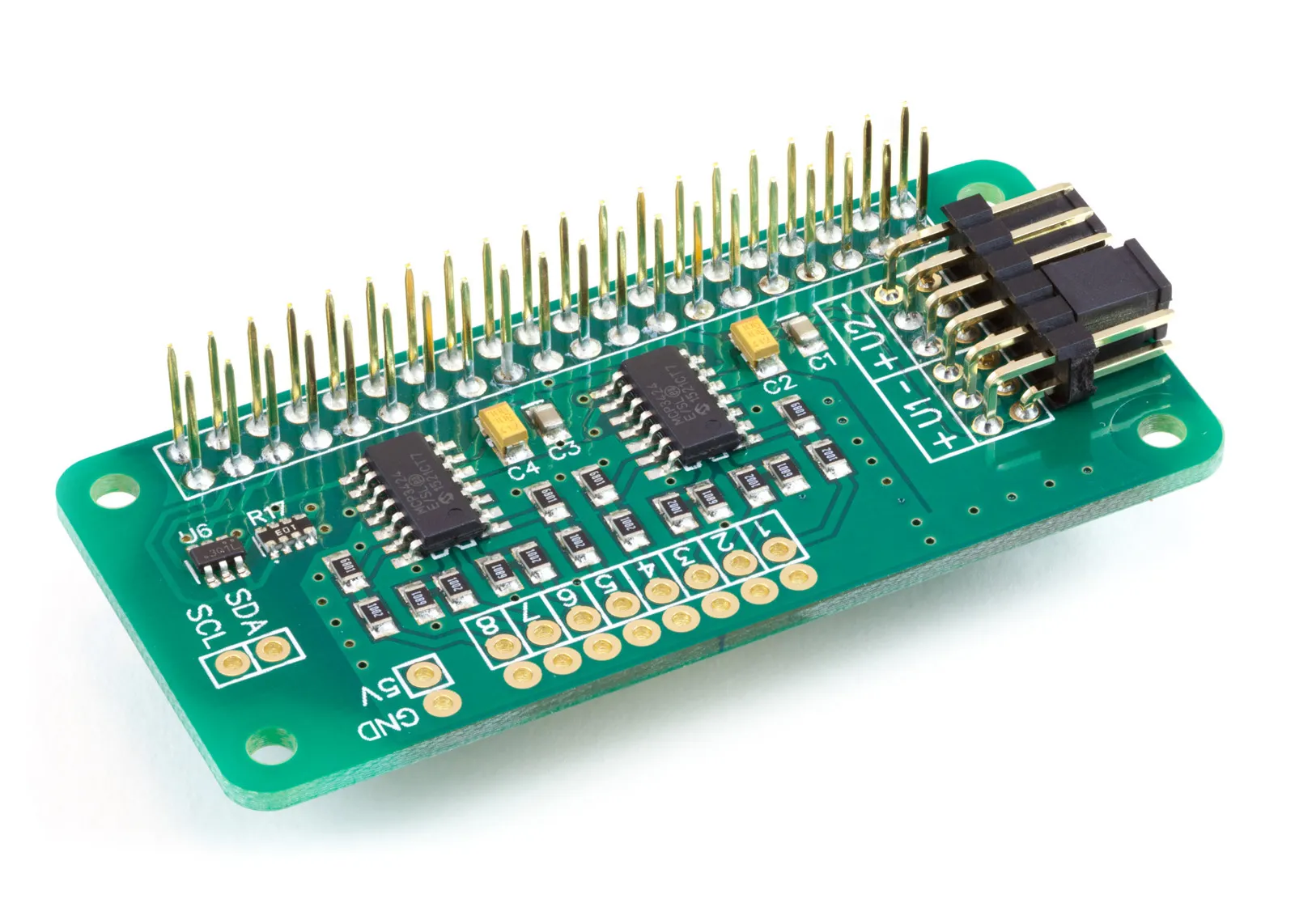
This tutorial will setup the ADC Pi to use with Home Assistant Operation System on your Raspberry Pi.
To integrate with Home Assistant you’ll need your Raspberry Pi plus the ADC Pi to provide analogue inputs.
This custom component is designed to run the ADC Pi Raspberry Pi development boards from AB Electronics UK with Home Assistant Operating System to add up to 32 analogue sensor inputs Home Assistant.
The ADC Pi is an 8 channel 17 bit analogue to digital converter designed to work with the Raspberry Pi. The ADC Pi is based on two Microchip MCP3424 A/D converters each containing 4 analogue inputs. This library uses our own ADC Pi Python library from abelectronics.co.uk/kb/article/23/python-library-and-demos
This component will enable the following platform.
- sensor: Show pin voltage via eight attributes.
I2C Support Required
First you will need to enable I2C support in the Home Assistant Operating System, we have a tutorial to enable I2C.
Installation and Configuration
To be able to install the custom components for the ADC Pi you need to be able to edit files in your configuration directory / folder.
We recommend using either the Samba add on or Studio Code Server which allows you to use Visual Code within Home Assistant.
Download the custom component from GitHub and extract to a directory on your computer.
- Using your tool of choice, open the directory (folder) for your HA configuration (where you find configuration.yaml).
- If you do not have a custom_components directory (folder) there, you need to create it.
- In the custom_components directory (folder) create a new folder called abelectronicsadcpi.
- Copy all the files from the custom_components/abelectronicsadcpi/ directory (folder) to the new abelectronicsadcpi directory (folder).
- Restart Home Assistant
Using your HA configuration directory (folder) as a starting point you should now also have this:
custom_components/abelectronicsadcpi/__init__.py custom_components/abelectronicsadcpi/sensor.py custom_components/abelectronicsadcpi/ADCPI.py custom_components/abelectronicsadcpi/manifest.json
Example configuration.yaml
sensor:
- platform: abelectronicsadcpi
name: ADCPi
i2c_address: 0x68
i2c_address2: 0x69
pga: 1
bitrate: 18
scan_interval: 5
Usage
Sensor Configuration Variables
The sensor component uses the following variables to configure the ADC sensor
| Key | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
i2c_address |
Hex |
True |
This contains the I2C address of the ADC Pi device. The default I2C addresses on the ADC Pi are 0x68 and 0x69. This address selects inputs 1 to 4. |
i2c_address2 |
Hex |
True |
This contains the I2C address of the ADC Pi device. The default I2C addresses on the ADC Pi are 0x68 and 0x69. This address selects inputs 5 to 8. |
pga |
Integer |
True |
Set the gain of the PGA on the chip. 1, 2, 4 or 8. |
bitrate |
Integer |
True |
This contains the selected bitrate for samples, this can be 12, 14, 16 or 18. Sample speeds for selected bit rate: 12 = 12 bit (240SPS max) 14 = 14 bit (60SPS max) 16 = 16 bit (15SPS max) 18 = 18 bit (3.75SPS max). |
scan_interval |
Integer |
True |
This contains the scan interval in seconds between reading the device in seconds. |
Editing the configuration.yaml file to add the binary sensor
Using the text editor of choice open the configuration.yaml for your HA configuration.
Add a new sensor with the following code:
sensor: - platform: abelectronicsadcpi
Add the following attributes to setup the component:
name: ADCPi i2c_address: 0x68 i2c_address2: 0x69 pga: 1 bitrate: 18 scan_interval: 5
Add the template sensor for the component to access the attributes:
- platform: template
sensors:
adcinput1:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input1}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 1"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput2:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input2}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 2"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput3:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input3}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 3"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput4:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input4}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 4"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput5:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input5}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 5"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput6:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input6}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 6"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput7:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input7}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 7"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput8:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input8}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 8"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
The completed YMAL code should look like this:
sensor:
- platform: abelectronicsadcpi
name: ADCPi
i2c_address: 0x68
i2c_address2: 0x69
pga: 1
bitrate: 18
scan_interval: 5
- platform: template
sensors:
adcinput1:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input1}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 1"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput2:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input2}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 2"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput3:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input3}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 3"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput4:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input4}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 4"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput5:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input5}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 5"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput6:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input6}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 6"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput7:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input7}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 7"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
adcinput8:
value_template: "{{states.sensor.adcpi.attributes.input8}}"
friendly_name: "ADC input 8"
unit_of_measurement: "Volts"
After a restart you can now add the sensor into the user interface.
Demo UI Cards
type: entities entities: - entity: sensor.adcinput1 - entity: sensor.adcinput2 - entity: sensor.adcinput3 - entity: sensor.adcinput4 - entity: sensor.adcinput5 - entity: sensor.adcinput6 - entity: sensor.adcinput7 - entity: sensor.adcinput8